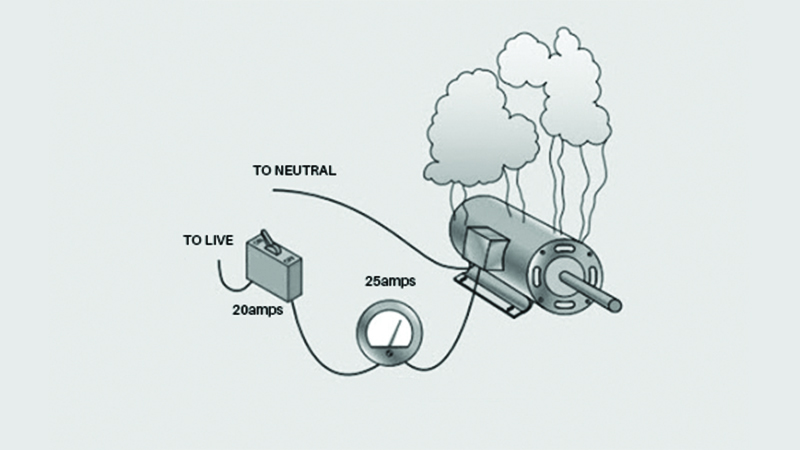
CASE STUDY
Low Power Factor
Reason: Power factor determines the distribution losses. It becomes low when you have Faulty capacitor, heavy machinery, Faulty wiring, Harmonics in Machines, Running Over Capacity in wires, etc.Issue: Penalties from Electricity board for PF below 0.9. Even if PF is maintained above 0.9, the PF Incentive amount can vary and be a loss for lesser incentives.
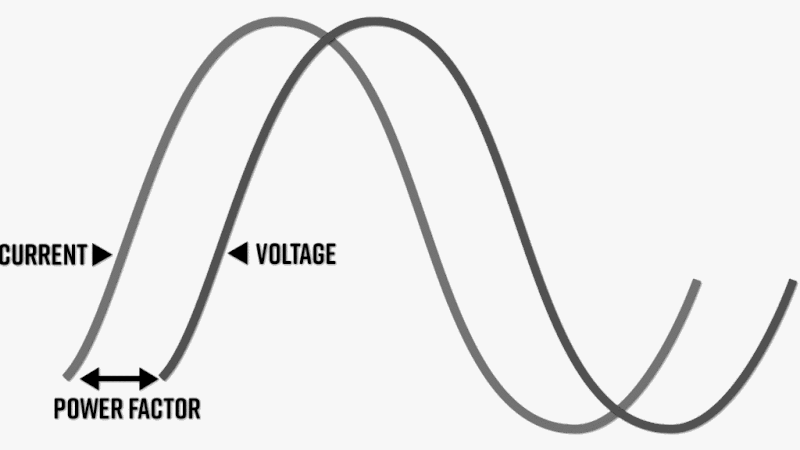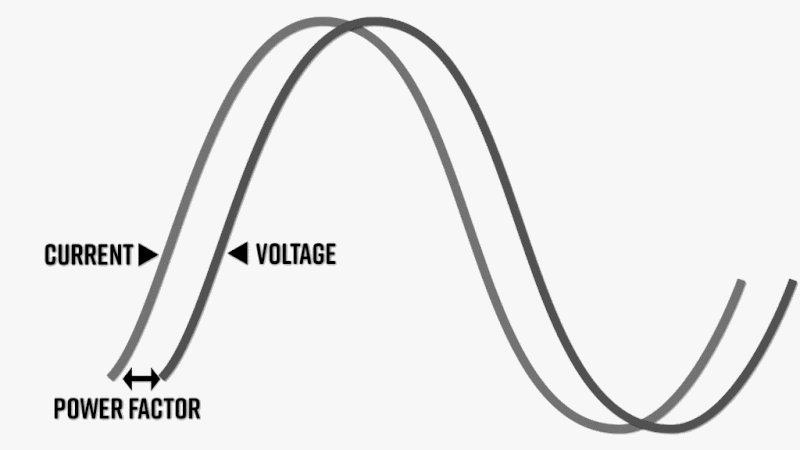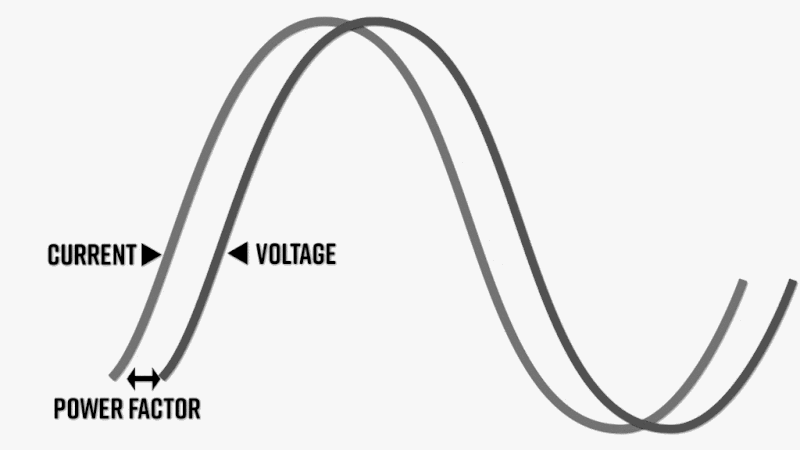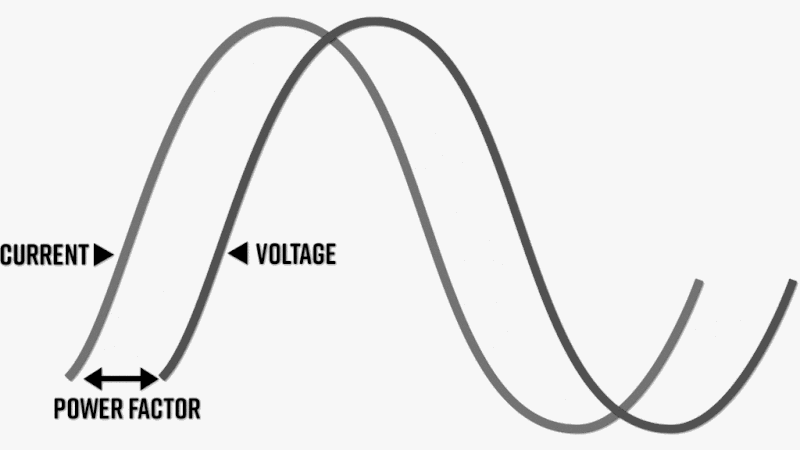
What is Power Factor?
Power factor is the phase difference between the voltage and current. If the current leads the voltage it is called leading power factor. It occurs when there is a reactive power generation near the load. If the current lags the voltage, it is called lagging power factor. It occurs when there is a reactive power absorption by the load. Normally the leading power factor is prevented while lagging power factor is allowed to a certain extent.
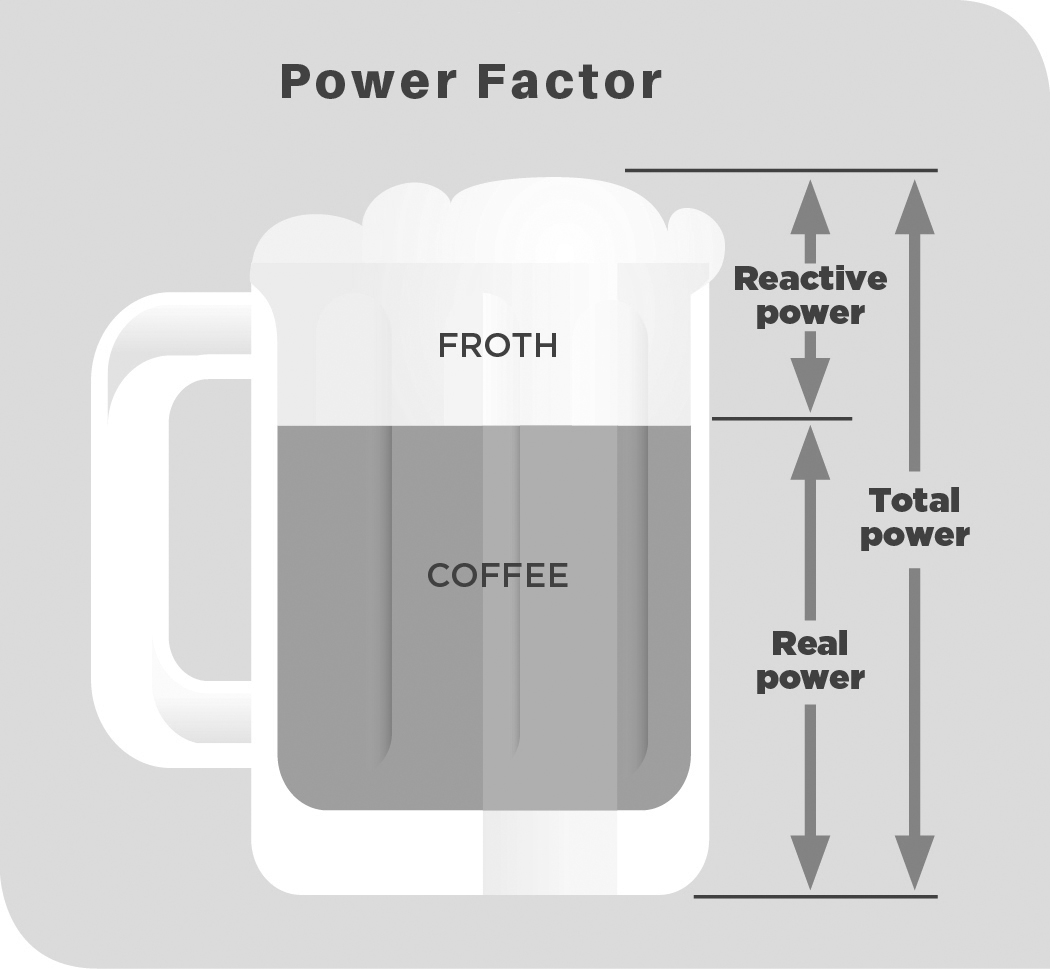
Power factor (PF) is an expression of energy efficiency. PF is the ratio of working power to apparent power. Apparent power, also known as demand, is the measure of the amount of power used to run machinery and equipment during a certain period.
PF expresses the ratio of true power used in a circuit to the apparent power delivered to the circuit.
Contract Demand Penalty
Reason: Fixed contract between Electricity board and the consuming party.Issue: If we exceed contract demand, we are charged at double the unit rate of normal. In two part tariff system, you will need to pay a fixed minimum based on the contract demand plus actual energy (KWH) charges. Even if you cross this limit once in a month, you will have to pay penalty for the month.
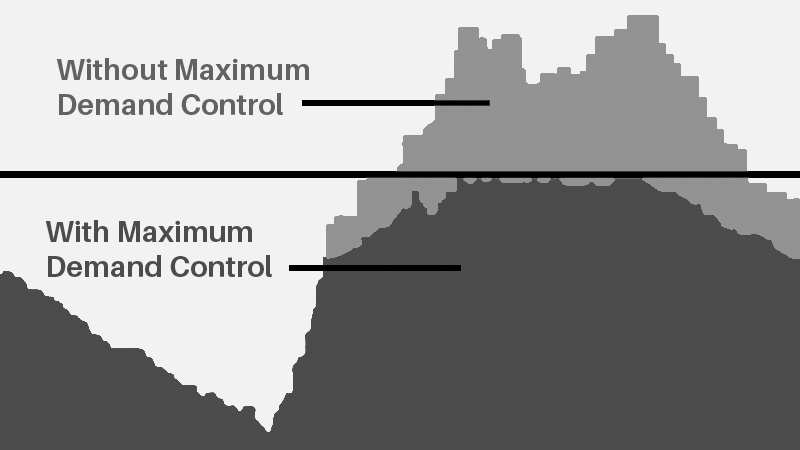
What is Contract Demand?
The contract demand is "the demand in Kilowatt (KW) or Kilo-voltAmpere (KVA) mutually agreed between the electricity company and the consumer as entered into the agreement or agreed through other written communication.
The maximum demand value is the average from the instantaneous power (in kW or kVA) during a defined time interval, usually every 15 minutes (this average time may vary depending on the company). Once the value is higher than the contracted power, the customer will pay a penalty on the electricity bill. Even if you cross this limit once in a month, you will have to pay penalty for the month.
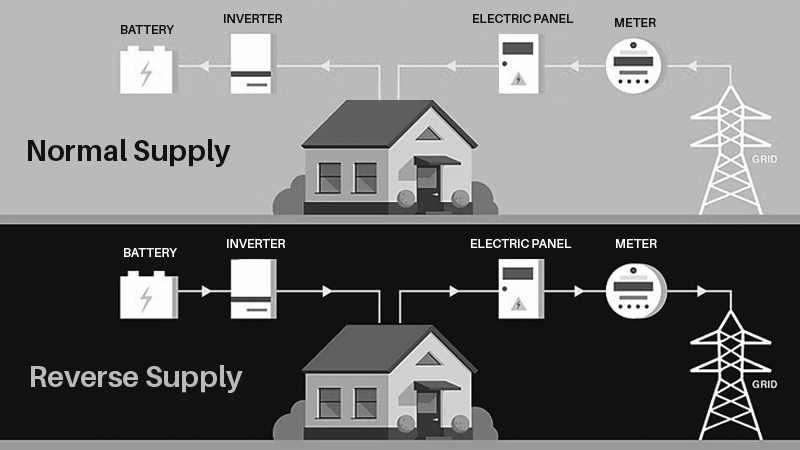
Reverse Supply
Reason: Capacitor and other charge storing devices might act as an energy source.Issue: Wastage of electric power and costs involved.
What is Revese Supply?
Reverse Supply may occur when the power provided by the electrical generator is able to flow over the electrical service line. Because an electrical transformer is capable of operating in both directions, electrical power generated from equipment on the consumer's premises can backfeed through the transformer and energize the distribution line to which the transformer is connected.
Motor Damage
Reason: Motor damages due to issues like One phase down, Low voltage fluctuations, High voltage fluctuations throughout the day.Issue: Winding damage, Increased harmonics, High consumption and eventually Motor failure.
How Motor Damage accurs?
Low quality of electricity may leads to breakdowns or malfunctions of machines, overheating of machines (transformers, motors, etc.), damage to sensitive equipment (computers, production line control systems, etc.), increased distribution system losses, the need to oversize systems to cope with additional electric stress, resulting in higher installation and operational costs, luminosity flickering
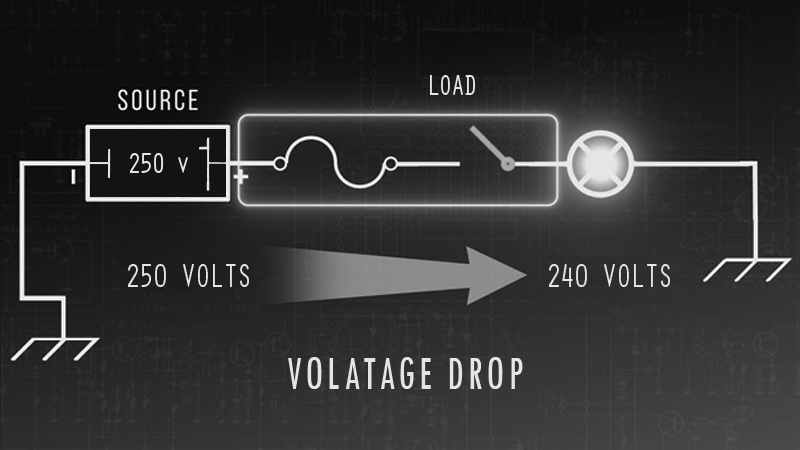
Voltage Drop
Reason: Due to faulty wiring, Excessive load, Type of wires used, its age, etc. voltage dropsIssue: Due to voltage drop, Current consumption of motors and devices increases which can heatup and reduce their life span.
Hazards of Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop across feeder and branch circuit can quickly reduce the output voltage of the power supply to an unacceptable limit. Because operating electrical equipment outside of its acceptable voltage rating can lead to premature equipment failure and hazardous situations.
Faulty Capacitor
Reason: Capacitors have a lifespan and can get damaged over time.Issue: Faulty Capacitor can cause heavy penalties from Electricity board and looking at the data we can come to know the Capacitor status.
What is faulty capacitor?
Capacitors are often thought of as the same category of electrical equipment as transformer and reactors. They are very different. Capacitors are actually electronic devices having significantly lower temperature capabilities and electrical insulation properties than either transformers or reactors. Three prominent factors that cause early failures of AC capacitors used in power factor or harmonic filter systems are: excessive voltage, excessive current and excessive temperature.

Over Capacity
Reason: Losses incurred.Issue: Eg. if 150 Amps flow in a wire with capacity of 100 Amps, it heats up, can even burn and can induce losses.